Java Installation
Java is a collection of software better known for
its cross platform availability was developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995. Java
platform is used by millions of applications and websites (specially used in
banking sites) due to its fast, secure and reliable nature.
Today, Java is everywhere, from desktops to
data-centers, game consoles to scientific computers, mobile phones.
There are more than one version of Java can be
installed and running on same computer and also it’s possible to have different
version of JDK and JRE simultaneously on a machine, actually there are abundant
of applications that requires Java-jre (Java Runtime Environment) and those who
are developer required Java-sdk (Software Development Kit).
There are lots of Linux distribution comes with
other version of Java called OpenJDK. OpenJDK is an open source implementation
of Java application.
Follow
these steps to download and install 32/64 - bit Java for Linux.
- Download
- Install
Download
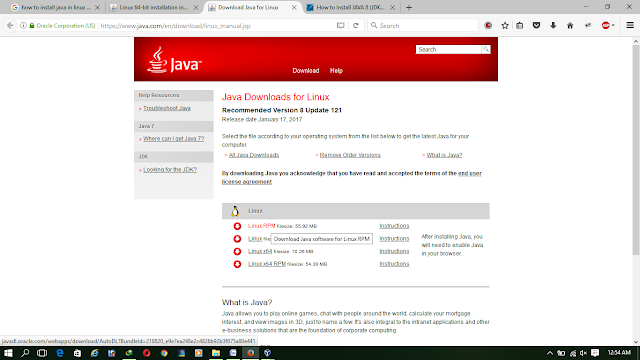
Go to http://java.com and click on the Download
button
Now download the Java (JDK) 8u45 source tarball
files for your system architecture as following Screenshot.
There
are two types of installation packages.
- Java on Linux Platforms
This installs
the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) for 32-bit Linux, using an archive binary
file (.tar.gz).
- Java on RPM-based Linux Platforms
- This installs the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) for 32-bit RPM-based Linux platforms, such as SuSE and Red Hat , using an RPM.
- Download the package that best pack your needs. You can download the file to any of the directories on your system.
- Before the file can be downloaded, you must accept the license agreement.
- Download and check the download file size to ensure that you have downloaded the full.
Install
Java 8 in Linux.
Note
:
To install Java in a system-wide location such as /usr/local, you must login as
the root user to gain the necessary permissions. If you do not have root
access, install the Java in your home directory or a sub directory for which
you have write permissions
Before installing Java, make sure that have you
installed java or verify the version of
installed Java.
|
[root@linuxelearn
~]# # java -version
java
version "1.7.0_75"
OpenJDK
Runtime Environment (IcedTea 2.5.4) (7u75-2.5.4-2)
OpenJDK
64-Bit Server VM (build 24.75-b04, mixed mode)
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
If Java is already installed, we will get the
current version.
Make a directory where you want to install Java. For
global access (for all users) install it preferably in the directory /opt/java.
#
mkdir /opt/java && cd /opt/java
|
[root@linuxelearn
~]# mkdir /opt/java
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
Change
to the directory in /opt/java.
Syntax
: # cd directory_path_name
For example, to install the software in the /opt/java/
directory type following command .
#cd
/opt/java/
|
[root@linuxelearn
~]# cd /opt/java
[root@linuxelearn
java]#
|
Move the downloaded .tar.gz archive binary to the
current directory.
Unpack
the tarball and install Java using following command.
#
tar zxvf jre-8u121-linux-i586.tar.gz
|
[root@linuxelearn
java]# tar zxvf jre-8u121-linux-i586
|
- The Java files are installed in a directory called jre1.8.0_73 in the current directory.
- Into this example, we have installed into /opt/java/jre1.8.0_73 directory.
- Delete the .tar.gz file if you want other wise you can keep as it is.
Java
on RPM based Linux
- First you have to Become root by running su and entering the super-user password.
- If you installed any previous Java packages in linux uninstall that packages using the following command.
#
rpm -e package_name
|
[root@linuxelearn
java]# rpm -e jre-8u121-linux-i586
|
3. Then Change to the directory in which you want to
install java packages using
Syntax:
cd directory_pat
For example, to install the software in the /opt/java/
directory.
#cd
/opt/java
|
[root@linuxelearn
~]# cd /opt/java
[root@linuxelearn
java]#
|
4. Install the java package using following command.
#rpm
-ivh jre-8u73-linux-i586.rpm
|
[root@linuxelearn
java]# rpm -ivh jre-8u121-linux-i586.rpm
Preparing...
########################################### [100%]
1:jre1.8.0_121
########################################### [100%]
Unpacking
JAR files...
plugin.jar...
/var/tmp/rpm-tmp.h1cXub:
/usr/java/jre1.8.0_121/bin/unpack200: /lib/ld-linux.so.
|
Use following command To upgrade a package,
#rpm
-Uvh jre-8u73-linux-i586.rpm
|
[root@linuxelearn
java]# rpm -Uvh jre-8u121-linux-i586.rpm
Preparing...
########################################### [100%]
package
jre1.8.0_121-1.8.0_121-fcs.i586 is already installed
[root@linuxelearn
java]#
|
- Exit from the root shell there is no need to reboot system.
Now set the Java Environment Variables.
|
[root@linuxelearn
java]# export JAVA_HOME=/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/
[root@linuxelearn
java]# export JRE_HOME=/opt/java/jdk1.8.0._45/jre
[root@linuxelearn
java]# export
PATH=$PATH:/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/bin:/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/jre/bin
|
#
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/
#
export JRE_HOME=/opt/java/jdk1.8.0._45/jre
#
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/bin:/opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/jre/bin
Now You can verify the Java version again, to
confirm.
# java -version
|
[root@linuxelearn
java]# java -version
java
version "1.8.0_45"
Java(TM)
SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_45-b14)
Java
HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.45-b02, mixed mode)
[root@linuxelearn
java]#
|
How
to enable Java Support in Firefox
You have to run following commands to enable Java
module for Firefox.
|
[root@linuxelearn
java]# alternatives --install /usr/lib/mozilla/plugins/libjavaplugin.so
libjavaplugin.so /opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/jre/lib/i386/libnpjp2.so 20000
|
---------------
For 32-bit Systems ---------------
#
alternatives --install /usr/lib/mozilla/plugins/libjavaplugin.so
libjavaplugin.so /opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/jre/lib/i386/libnpjp2.so 20000
---------------
For 64-bit Systems ---------------
#
alternatives --install /usr/lib/mozilla/plugins/libjavaplugin.so
libjavaplugin.so /opt/java/jdk1.8.0_45/jre/lib/amd64/libnpjp2.so 20000
Now check the Java support by restarting Firefox and
enter about:plugins on the address
bar. You will get following screen output.
........................................................
I hope You enjoyed reading this article.





Post a Comment