Adding user to a Group
Add a User to a Group (or Secondary Group) on Linux
Changing the group of user is associated to is a very easy task, but not
everybody knows the commands, especially to add a user to a secondary group. In
this tutorial we will learn about all user and group related commands.
You can use
the useradd or usermod commands to add a user to a group. The useradd command
creates a new user or update default new user information. The usermod command
modifies a user account and it is useful to add user to existing groups. There
are two types of groups under Linux operating systems:
- Primary user group.
- Secondary or supplementary user group.
All user
account related information are stored in the following files:
- /etc/passwd – Contains one line for each user account.
- /etc/shadow – Contains the password information in encrypted formatfor the system’s accounts and optional account aging information.
- /etc/group – Defines the groups on the system.
- /etc/default/useradd – This file contains a value for the default group, if none is specified by the useradd command.
- /etc/login.defs – This file defines the site-specific configuration for the shadow password suite stored in /etc/shadow file.
How to Add a new user to secondary group
In this
example, create a new user called rahul and add it to group called admin. First
login as a root user (make sure group admin exists or not ), :
# grep admin /etc/group
Sample outputs:
# grep admin /etc/group
Sample outputs:
[root@linuxelearn
~]# grep admin /etc/group
desktop_admin_r:x:497:
admin:x:507:
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
If you do not see any output then you need to add group admin group using the groupadd command:
How to Add a New Group To read Full article about this click here
To add a new group into system, all you need to do is use the groupadd command like so:
#groupadd <groupname>
[root@linuxelearn
~]# groupadd admin
|
When you create a group then add that group to user (rahul) using usermod linux command.
[root@linuxelearn
~]# usermod -G admin rahul
|
How to add an Existing User to a Group
Frist check
that user rahul exists or not :
# grep ^rahul /etc/passwd
Next we are trying to add a user to the group, using this syntax:
#usermod -a -G <groupname> username
For example, to add user rahul to the group admin, use the following command:
# grep ^rahul /etc/passwd
Next we are trying to add a user to the group, using this syntax:
#usermod -a -G <groupname> username
For example, to add user rahul to the group admin, use the following command:
[root@linuxelearn
~]# usermod -a -G admin nagios
|
How can I change a User’s Primary Group
Sometimes you might want to switch out the primary group that a user is assigned to, which you can do with this usermod command:
#usermod -g <groupname> username
[root@linuxelearn
~]# usermod -g rpgroup nagios
|
Add a New User and Assign a Group in One Command
Sometimes you might need to add a new user that has access to a particular resource or directory, like adding a new FTP user. You can do so with the useradd command:
#useradd -g <groupname> username
Now you are trying to add a new user named pooja to the ftp group:
#useradd -G ftp pooja
[root@linuxelearn
~]# useradd -G ftp pooja
|
And then you want to assign a password for that user, of course:
#passwd Username
[root@linuxelearn
~]# passwd pooja
Changing
password for user pooja.
New
password:
BAD
PASSWORD: it is based on a dictionary word
Retype
new password:
passwd:
all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
Add a User to Multiple Groups
You can easily add a user to more than one group by simply specifying them in a comma-delimited list, as long as you are assigning the secondary groups:
#usermod -a -G ftp,admin,nagios <username>
[root@linuxelearn
~]# usermod -a -G ftp,admin,nagios pooja
|
Please note
that capital G (-G) option add user to a list of supplementary groups. Each
group is separated from the next by a comma, with no intervening whitespace. For
example, add user rahul to groups admin, ftp, and nagios.
View a User’s Group Assignments
If you’re trying to figure out a permissions issue, you’ll want to use the id command to see what groups the user is assigned to:
#id <username>
This will display output something like this:
If you’re trying to figure out a permissions issue, you’ll want to use the id command to see what groups the user is assigned to:
#id <username>
This will display output something like this:
[root@linuxelearn
~]# id pooja
uid=503(pooja)
gid=508(pooja) groups=508(pooja),504(ftp),505(nagios),507(admin)
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
You can also use the groups command if you like, though it is the same as using id -Gn <username>.
#groups <username>
[root@linuxelearn
~]# groups pooja
pooja
: pooja ram rpgroup admin
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
How to Check a List of All Groups
To view all the groups on the system, you can just use the groups command:
#groups
[root@linuxelearn
~]# groups
root
bin daemon sys adm disk wheel
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
How to remove or delete a user from the group
#gpasswd –d <username> <groupname>
#gpasswd –d pooja admin
[root@linuxelearn
~]# gpasswd -d pooja admin
Removing
user pooja from group admin
[root@linuxelearn
~]# grep admin /etc/group
desktop_admin_r:x:497:
admin:x:507:nagios
[root@linuxelearn
~]#
|
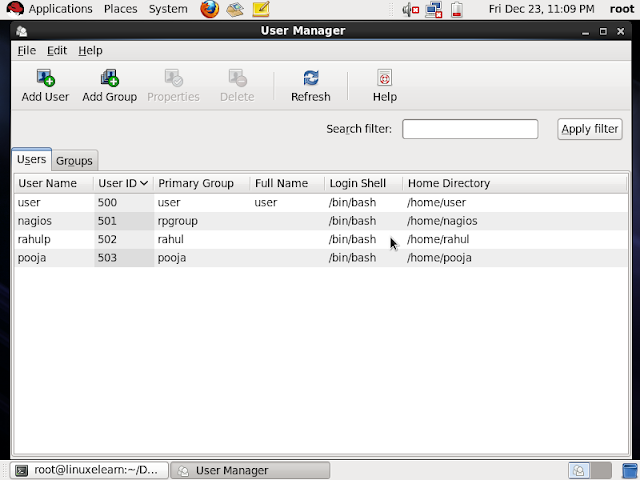
To Add and
remove users and groups you can also use the graphical tool in Linux
#system-config-users
This article cover everything you need to know about adding users to groups on Linux. If you like this article and any suggestion then comment and share please...




Post a Comment