To create file with size you can use following commands on different platform.
On Solaris, you can use this command:
$ mkfile file-size
file-name
$ mkfile 10m
output.dat
|
dd if=/dev/zero
of=output.dat bs=24M count=1
or
dd if=/dev/zero
of=output.dat bs=1M count=24
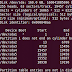
[root@kernal ~]# dd if=/dev/zero of=file.example
bs=10M count=1
1+0 records in
1+0 records out
10485760 bytes (10 MB) copied, 0.0559974 s,
187 MB/s
|
For Check size of the file:
[root@kernal ~]# ls -hl file.example
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 10M Jul 26 19:47 file.example
|
Under non-embedded Linux or Cygwin (or any
system with GNU coreutils) and FreeBSD:
# truncate -s 10G
file-name
[root@kernal ~]# truncate -s 20m file
[root@kernal ~]#
[root@kernal ~]# ls -hl file
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 20M Jul 26 19:57 file
|
This creates a file
full of null bytes. If the file already exists and is smaller, it is extended
to the requested size with null bytes. If the file already exists and is
larger, is is truncated to the requested size.
The null bytes do not
consume any disk space, the file is a sparse file.
# fallocate -l 5G
file-name
[root@kernal
~]# fallocate -l 25M
file1
[root@kernal
~]# ls –hl file1
-rw-r--r--
1 root root 25M Jul 26 19:57 file1
|
You
can do it using Program:
#include
<unistd.h>
#include
<sys/types.h>
#include
<sys/stat.h>
#include
<fcntl.h>
#include
<stdlib.h>
int
main() {
int fd = creat("/tmp/foo.txt",
0644);
ftruncate(fd, SIZE_IN_BYTES);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
|
This is
useful to subsequently mmap the file into memory.
use the following command to check file size:
#
du -B1 --apparent-size /tmp/foo.txt
|
OR
#
du /tmp/foo.txt
|
It will print 0 because it is allocated as Sparse
file if supported by your filesystem.
Linux Interview Questions And Answers
Linux Interview Questions And Answers





Post a Comment